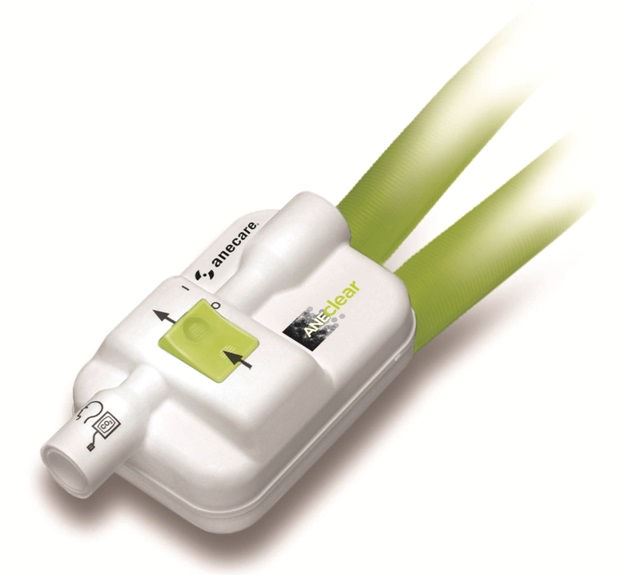
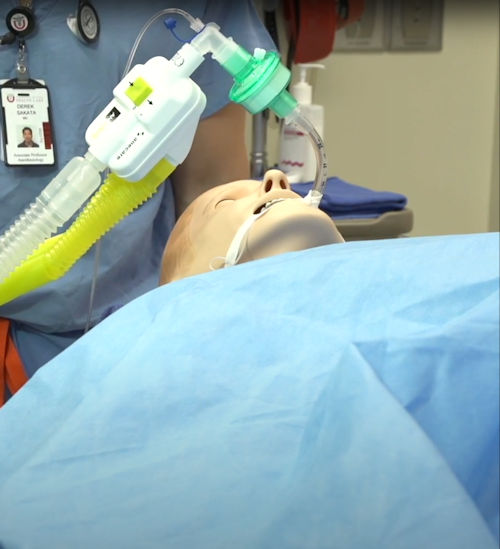
ANEclear
Designed to clear inhaled anesthetics from the brain at the end of surgery.
ANEclear reverses the effects of inhaled anesthetics in the brain at the end of surgery for a safer, smoother, quicker recovery for your elderly, obese or pediatric patient.

ANEclear
Designed to clear inhaled anesthetics from the brain at the end of surgery.
ANEclear reverses the effects of inhaled anesthetics in the brain at the end of surgery for a safer, smoother, quicker recovery for your elderly, obese or pediatric patient.
Overview
There are no drugs designed to bring patients out of the effects of inhaled volatile anesthetics. Tapering these anesthetics off at the end of surgery discontinues delivery, but requires clinicians and patients to wait for the effects to wear off, resulting in on-going exposure in the brain. On-going exposure contributes to delirium, postoperative cognitive dysfunction, airway complications, and nausea and vomiting.1,2
 Mechanism of general anesthesia
Mechanism of general anesthesia
Recently published research (2020) confirms that volatile anesthetics alter ion channel function in cells, which impedes electrical signaling in the neurons that control wakefulness and breathing, resulting in a loss of consciousness.10
Effect of CO2 on anesthetics and neurons
Carbon dioxide has been shown to vasodilate the cerebral vasculature, and to restore electrical signaling in neurons in the brain that control wakefulness and breathing. 11,12,13
ANEclear technology activates the brain
ANEclear’s patented process uses the patient’s own carbon dioxide to reverse the effects of inhaled volatile anesthetics in the brain, using a two-step process; 1) vasodilating the cerebral vasculature accelerating washout of anesthetics, and 2) reversing the effects these anesthetics have on neurons that control consciousness and breathing.
 Mechanism of general anesthesia
Mechanism of general anesthesia
Recently published research (2020) confirms that volatile anesthetics alter ion channel function in cells, which impedes electrical signaling in the neurons that control wakefulness and breathing, resulting in a loss of consciousness.10
Effect of CO2 on anesthetics and neurons
Carbon dioxide has been shown to vasodilate the cerebral vasculature, and to restore electrical signaling in neurons in the brain that control wakefulness and breathing. 11,12,13
ANEclear technology activates the brain
ANEclear’s patented process uses the patient’s own carbon dioxide to reverse the effects of inhaled volatile anesthetics in the brain, using a two-step process; 1) vasodilating the cerebral vasculature accelerating washout of anesthetics, and 2) reversing the effects these anesthetics have on neurons that control consciousness and breathing.
ANEclear’s proprietary technology

Benefits
Better patient outcomes, workflow, and lower costs
Rapid reversal of volatile anesthetics from the brain following surgery reduces the effects these anesthetics have on patients during recovery, which includes delirium, respiratory complications associated with Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA), and Post Operative Nausea and Vomiting (PONV). These complications increase the risk of neurocognitive dysfunction, prolonged postoperative stay, unanticipated admissions, and increased costs.
ANEclear benefits
- Accelerates washout of anesthetics from the brain
- Returns brain function and consciousness
- Increases spontaneous drive to breathe
- Provides a fast, smooth anesthesia recovery
- Lowers risk of complications
- Increases OR / PACU performance
- Lowers cost of patient care
- Reduces exposure to the environment and staff
from waste anesthetic gas

Seniors – At risk for delirium, cognitive dysfunction, and airway complications
1 in 10 surgical patients are age 65 or older. The aging brain is more vulnerable to anesthesia. Older patients are at higher risk of the following complications.14
- Postoperative delirium – A temporary condition that causes patients to be confused, disoriented, and experience memory problems.
- Postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD) – A more serious condition that can lead to long-term memory loss making it difficult to learn, concentrate, and think.
- Airway complications – older adults over age 65 are 2x more likely to have OSA.15
Obese – At risk for airway complications associated with Obstructive Sleep Apnea
According to the CDC 39.8% of U.S. adults are obese. These individuals are at increased risk of OSA and adverse airway events following surgery.
- Incidence of OSA in Surgery – Studies estimate that 24–41% of elective surgery patients are at risk for OSA.17
- OSA related airway risks – Risks associated with OSA and anesthesia include upper-airway obstruction, difficult tracheal intubation, postoperative respiratory depression, and airway obstruction.18
For older patients, ANEclear restores brain function, breathing, and consciousness to quickly return these patients to baseline for a safer recovery.
For obese patients, ANEclear restores wakefulness and breathing to increase the spontaneous drive to breathe and protect airway reflexes during recovery.

Seniors – At risk for delirium, cognitive dysfunction, and airway complications
1 in 10 surgical patients are age 65 or older. The aging brain is more vulnerable to anesthesia. Older patients are at higher risk of the following complications.14
- Postoperative delirium – A temporary condition that causes patients to be confused, disoriented, and experience memory problems.
- Postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD) – A more serious condition that can lead to long-term memory loss making it difficult to learn, concentrate, and think.
- Airway complications – older adults over age 65 are 2x more likely to have OSA.15
For older patients, ANEclear restores brain function, breathing, and consciousness to quickly return these patients to baseline for a safer recovery.

Obese – At risk for airway complications associated with Obstructive Sleep Apnea
According to the CDC 39.8% of U.S. adults are obese. These individuals are at increased risk of OSA and adverse airway events following surgery.
- Incidence of OSA in Surgery – Studies estimate that 24–41% of elective surgery patients are at risk for OSA.16
- OSA related airway risks – Risks associated with OSA and anesthesia include upper-airway obstruction, difficult tracheal intubation, postoperative respiratory depression, and airway obstruction.17
For obese patients, ANEclear restores wakefulness and breathing to increase the spontaneous drive to breathe and protect airway reflexes during recovery.
Resources
ANEclear eLearning Module
For quick reference, following are the five subsections contained in the eLearning Module: